The endocrine system acts through Chemical Messengers known as Hormones.
Definition of Hormones
- Hormone derived from the Greek word ‘hormacin’, meaning to excite.
- An organic substance synthesised in small amounts by specific tissues (endocrine glands) & transported by the circulatory system to act on another tissue (target cells).
Classification of Hormones
Based on chemical nature:
- Protein or peptide hormones :
- Insulin, Glucagon, Growth hormone, ADH, Oxytocin.
- Steroid hormones :
- Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids, Sex hormones.
- Amino acid derivatives:
- Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, T3 & T4
Based on solubility properties:
- Lipophilic: Ex- Steroids, thyroid hormones
- Hydrophilic: Ex- Insulin, growth hormone, ADH
Based on mechanism of action:
Group I hormones – Mostly Lipophilic
-
- Can easily traverse across the cell membrane
- Binds to intracellular receptors.
- Hormone-receptor complex enters the nucleus, binds to DNA and causes gene expression.
Group II hormones – Mostly Hydrophilic
-
- Cannot traverse the cell membrane
- Binds to cell surface receptors.
- Cell surface (plasma membrane) receptor
- Hormone itself is a first messenger.
- Mediator or Intermediary molecules are second messengers.
- Hormone-receptor complex stimulates the release of secondary messengers which exert the biochemical function.
-
-
- cAMP
- cGMP.
- Calcium and phosphatidyl inositol
- Kinase or phosphatase
-
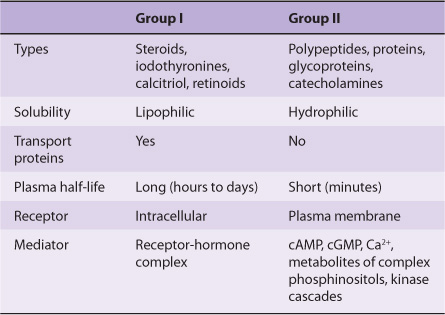 Fig: Difference between Group I and Group II hormones.
Fig: Difference between Group I and Group II hormones.
Examples of hormones:
Group I hormones:
Glucocorticoids, Mineralocorticoids, Estrogen, Progestin, Androgens,
Calcitriol (Vitamin D), Thyroid hormones (T3, T4), Retinoic Acid
Group II A: Second messenger is cAMP
ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH, PTH, hCG, Glucagon, Calcitonin, Epinephrine, Norepinephine
Group II B: Second messenger is cGMP
ANF, NO
Group II C: Second messenger is Ca or PI or both
Oxytocin, Vasopressin, Angiotensin II, Gastrin, Cholecystokinin
Group II D: Second messenger is a kinase or phosphatase cascade
GH, Insulin, Prolactin, Chorionic Somatomammotropin
Mechanism of Action of Group I Hormones
- Steroid hormones are lipophilic hormones belonging to Group I hormones. These hormones bind with receptors inside the cell rather than in the cell membrane. Because these hormones are lipid soluble, they readily cross the cell membrane and interact with receptors in the cytoplasm.
- The hormone receptor complex is assumed to be the intracellular messenger for these (Group I) hormones. The activated hormone receptor complex undergoes conformational change which then binds with a specific regulatory (promoter) sequence of DNA called the hormone response element (HRE) which activates transcription of specific genes and formation of mRNA. These mRNA get translate into proteins. Newly formed proteins in the cell controls the cellular metabolic functions.
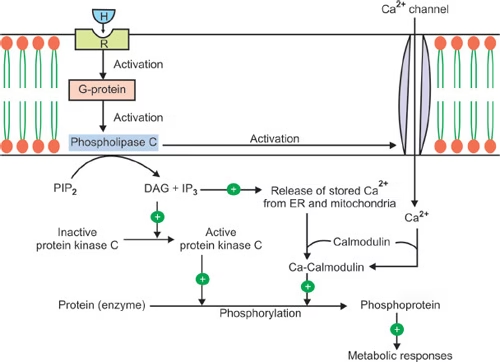 Fig: Mechanism of action of group I hormones
Fig: Mechanism of action of group I hormones
Mechanism of action of Group II Hormones
- These hormones are mostly hydrophilic.
- Receptors for this group of hormones are located on the cell surface (plasma membrane receptors). Since the hormone cannot enter the cell, the hormone–receptor complex stimulates the release of certain molecules known as second messengers in the cell which exert the hormone’s biochemical function. Here, the hormone itself is considered to be the first messenger.
- They have membrane receptors & use intracellular messengers.
- Water soluble hormones use cell surface receptors because cannot pass through plasma membrane
- Actions are mediated by 2nd messengers
- Hormone is extracellular signal; 2nd messenger carries signal from receptor to inside of cell
Group II. A: Second Messenger is cAMP
- The activated G-protein stimulates the membrane-bound enzyme, adenylyl cyclase, which in turn catalyses synthesis of cAMP from ATP. cAMP acts as the second messenger to various hormones.
- Once produced, cAMP activates protein kinase A (A stands for cAMP).
- Protein kinase A (PKA): Heterotetrameric- Two regulatory and two catalytic subunits
- PKA become active and phosphorylates the target proteins.
- cAMP undergoes rapid degradation catalysed by the enzyme phosphodiesterase to AMP which is biologically inert.
cAMP + R2C2 → R2. cAMP + C2
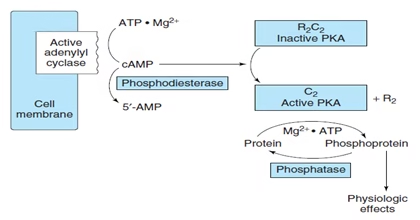 Fig: cAMP dependent protein kinases
Fig: cAMP dependent protein kinases
Protein phosphorylation:
Activated PKA phosphorylates a number of target proteins resulting in ultimate biological response. This phosphorylation undergoes dephosphorylation by enzyme protein phosphatase. In this way, hormone regulate metabolic pathway by protein phosphorylation-dephosphorylation.
Group II. B: Second Messenger is cGMP
A hormone called atrial natriuretic factor secreted by atrial tissue uses cGMP as second messenger.
Group II. C: Second Messenger is Ca or PI or both
The activated G-protein stimulates the membrane bound enzyme, Phospholipase C which hydrolyses the membrane phospholipids, into two components, Inositol Triphosphate (IP3) and diacyl glycerol (DAG). These two molecules act as second messenger for several hormones.
Inositol Triphosphate IP3:
Water soluble IP3, opens calcium channels and releases Ca++ from the ndoplasmic reticulum. Ca++ has several functions in the cell.
Diacylglycerol (DAG):
DAG, activates the membrane-bound enzyme, Protein kinase C (C for calcium, the enzyme depends on Calcium for its activity) which phosphorylates a number of target proteins eliciting the biological response.
Calcium and Calmodulin:
Ca++ mobilized from ECF endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria (caused by IP3) acts by binding to calmodulin and other calcium sensors. Ca++- Calmodulin activates enzymes (Protein kinase C, Calmodulin kinase) which enhance membrane excitability and cause musle contraction.
All these molecules, IP3, DAG, Ca++ and calmodulin acts synergistically in eliciting hormonal response at the cellular level.
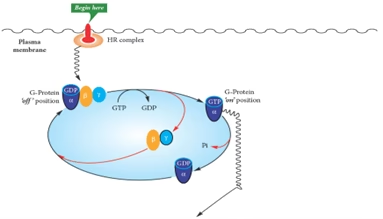
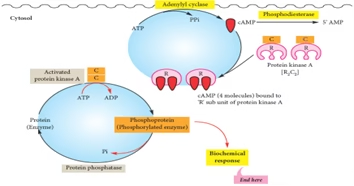 Fig: Mechanism of action of group II hormones using cAMP as second messenger
Fig: Mechanism of action of group II hormones using cAMP as second messenger