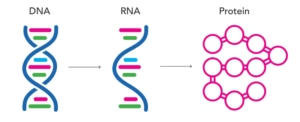
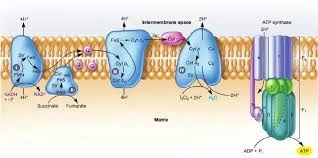
Micronutrients and Macronutrients: Micronutrients are substances required in very small amounts (mg or μg) and that mainly function as co-factors of enzymes ( < 0.005% body weight). Vitamins Trace minerals (Fe, I, Cu, Mn, Zn, Mo, Se, Mn, F). Macronutrients Read More …